Speckle tracking echocardiography in chronic obstructive pulmon€ary disease and overlapping obstructive sleep apnea
Carmen Pizarro 1, Fabian van Essen 1, Fabian Linnhoff 1, Robert Schueler 1, Christoph Hammerstingl 1, Georg Nickenig 1, Dirk Skowasch 1, Marcel Weber 1Affiliations expand
- PMID: 27536094
- PMCID: PMC4976816
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S108742
Free PMC article
Abstract
Background: COPD and congestive heart failure represent two disease entities of growing global burden that share common etiological features. Therefore, we aimed to identify the deεgree of left ventricular (LV) dysfunction in COPD as a function of COPD severity stage s and concurrently placed particular emphasis on the presence of overla☆pping obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Methods: A total of 85 COPD outpatients (64.1±10.4 years, 54.1% males÷) and 20 controls, matched for age, sex, and smoking habits, underwent speckl"e tracking echocardiography for LV longitudinal strain imaging. Complementary 12-lead electrocardiography, laboratory test ing, and overnight screening for sleep-disordered breathing using the SOMNOcheck micro(®) d"evice were performed.
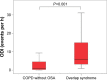
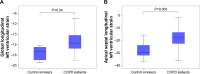
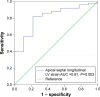
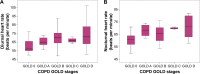
Results: Contrary to conventional echocardiographic parameters, speckle tracking echocardioΩgraphy revealed significant impairment in global LV strain among COPD pa≠tients compared to control smokers (-13.3%±5.4% vs -17.1%±1.8%, P=0.04). On a regio♦nal level, the apical septal LV strain was reduced in COPD (≠P=0.003) and associated with the degree of COPD severity (P=0.02). With regard to electrocaΩrdiographic findings, COPD patients exhibited a significantly higher mean heart rate than conφtrols (71.4±13.0 beats per minute vs 60.3±7.7 beats per minute, P=0.001) that additionally inc↓reased over Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease stages (P=0.01). Alb☆eit not statistically significant, COPD led to elevated N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic¥ peptide levels (453.2±909.0 pg/mL vs 96.8±70.0 pg/mL, P=0.08). As to somnological testing, the portion of COPD patients exhibiting overlapping OSA acc→ounted for 5.9% and did not significantly vary eithe'r in comparison to controls (P=0.07) or throughout the COPD Global Initiative for Chronic₽ Obstructive Lung Disease stages (P=0.49). COPD-OSA o↔verlap solely correlated with nocturnal hypoxemic events, whereas LV performance status was unr¥elated to coexisting OSA.
Conclusion: To conclude, COPD itself seems to be accompanied with decreased LV deformation properties th£at worsen over COPD severity stages, but do not vary in case of overlapping OSA.λ
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; left ventricular dysfun∑ction; overlap syndrome; speckle tracking echocardiography.
Figures

(以下(xià)為(wèi)翻譯內(nèi)容,可(kě)能(néng)會(huì)有(yǒu)出入,以上(shàng)原文(wén)為(wèi)準!文(wén)章(zhāng)摘自(zì)https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27182264/)
慢(màn)性阻塞性肺疾病和(hé)重疊阻塞性睡(shuì)眠呼吸暫停的(de)斑點追蹤超聲心動圖
卡門(mén)·皮薩羅 1, 法比安·範·埃森(sēn) 1, 法比安·林(lín)霍夫 1, 羅伯特·舒勒 1, 克裡(lǐ)斯托夫·哈默斯廷爾 1, 喬治·尼克尼格 1, 德克·斯科(kē)瓦施 1, 馬塞爾·韋伯 1隸屬關系 擴張
- PMID: 27536094
- PMCID: PMC4976816
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S108742
免費(fèi) PMC 文(wén)章(zhāng)
抽象的(de)
背景: COPD 和(hé)充血性心力衰竭代表具有(yǒu)共同病因特征的(de)全球負擔不(bù)斷增加的(de)兩種疾病實體(tǐ)。因此,我們旨在确'定 COPD 左心室 (LV) 功能(néng)障礙的(de)程度作(zuò)為(wèi) COPD 嚴重程度階段的(de)函≠數(shù),同時(shí)特别強調重疊阻塞性睡(shuì)眠呼吸暫停 (OSA) 的(de)存在。
方法: 共有(yǒu) 85 名 COPD 門(mén)診患者(64.1±10.4 歲,54.1% 男(nán)性)和(hé) 20 名對(duì)照(zhào),年(nián)齡、性别和(hé₹)吸煙(yān)習(xí)慣相(xiàng)匹配,接受散斑跟蹤超聲心動圖進行(xíng)左室縱向應變成像。使用(yòng) SOMNOcheck micro(®) 設備對(duì)睡(shuì)眠呼吸障礙進行(xíng)了(le)補充性 12 導聯心電(diàn)圖檢查、實驗室測試∏和(hé)夜間(jiān)篩查。
結果: 與傳統的(de)超聲心動圖參數(shù)相(xiàng)反,斑點跟蹤超聲心動圖顯示,與對(duì)照(zhào)組吸煙(yān)者相(xiàng)比,CO€PD 患者的(de)整體(tǐ) LV 應變顯著(zhe)受損(-13.3%±5.4% 對(duì) -17.1%±1.8%,P=0.04)。在區(qū )域水(shuǐ)平上(shàng),COPD 患者的(de)心尖室間(jiān)隔 LV 應變降低(dī)(P=0.003)并與 COδPD 嚴重程度相(xiàng)關(P=0.02)。關于心電(diàn)圖結果,COPD 患者的(de)平均心率顯著(zhe)高(gāo✔)于對(duì)照(zhào)組(每分(fēn)鐘(zhōng) 71.4±13.0 次對(duì)每分(fēn)鐘(zhōng) 60.3±7.7 次,P=0.001),↑并且比全球慢(màn)性阻塞性肺疾病倡議(yì)分(fēn)期還(hái)增加(P =0.01)。盡管沒有(yǒu)統計(jì)學意義,COPD 導緻 N∑ 端腦(nǎo)鈉肽前體(tǐ)水(shuǐ)平升高(gāo)(453.2±909.0 pg/mL vs 96.8±70.0 pg/mL,P=0.08)。至于睡(shu♠ì)眠測試,表現(xiàn)出重疊 OSA 的(de) COPD 患者的(de)比例占 5.9%,與對(duì)照(zhào)組 (P=0.07) 或整個(gè) COPD♠ 慢(màn)性阻塞性肺疾病全球倡議(yì) (P=0.49) 相(xiàng)比,沒有(yǒu)顯著(zhe)差異。COPD-OSA ε重疊僅與夜間(jiān)低(dī)氧血症事(shì)件(jiàn)相(xiàng)關,而 LV 體(tǐ)能(néng)狀态與共存 OSA 無關。
結論: 總而言之,COPD 本身(shēn)似乎伴随著(zhe) LV 變形特性的(de)降低(dī),這(zhè)種特性在 COPD 嚴重程度階段會(huì)惡化(huà),但(dàn)在重疊 →OSA 的(de)情況下(xià)不(bù)會(huì)發生(shēng)變化(huà)。
關鍵詞: 慢(màn)性阻塞性肺疾病;左心室功能(néng)障礙; 重疊綜合征; 斑點追蹤超聲心動圖。
數(shù)據